how to know what table value to use bond price issue
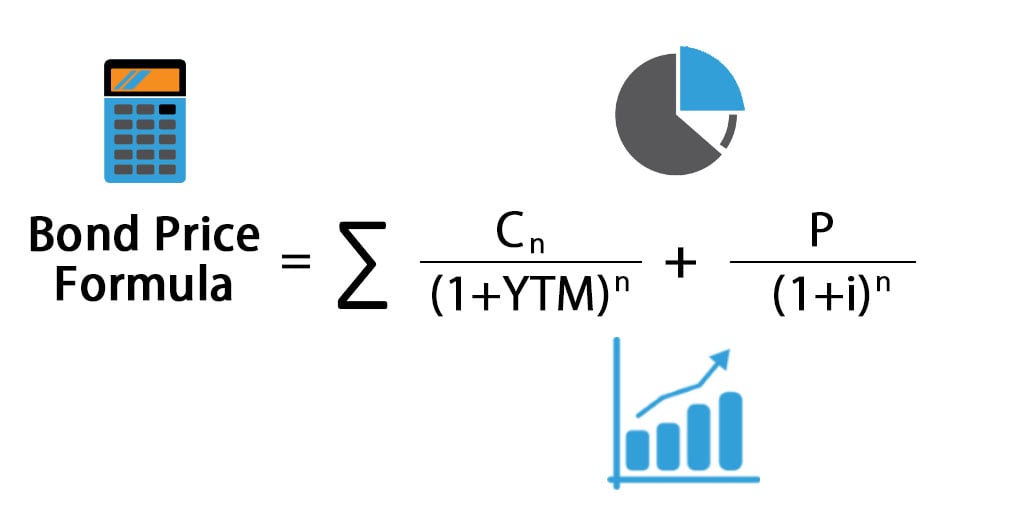
Bail Pricing Formula(Table of Contents)
- Bond Pricing Formula
- Examples of Bond Pricing Formula (With Excel Template)
Bond Pricing Formula
Bond pricing is the formula used to calculate the prices of the bond being sold in the main or secondary market.
Bond Price = ∑(Cn/ (i+YTM)n )+ P / (one+i)due north
Where
- n = Period which takes values from 0 to the nth period till the greenbacks flows ending period
- Cnorth = Coupon payment in the nth period
- YTM = interest rate or required yield
- P = Par Value of the bond
Examples of Bail Pricing Formula (With Excel Template)
Let's take an example to understand the calculation of Bail Pricing in a better style.
Y'all tin download this Bond Pricing Formula Excel Template here – Bail Pricing Formula Excel Template
Bond Pricing Formula – Example #i
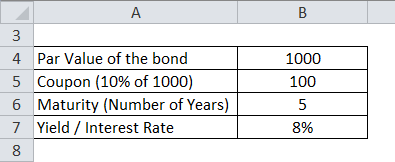
Let'southward calculate the cost of a bond which has a par value of Rs grand and coupon payment is 10% and the yield is 8%. The maturity of a bail is 5 years.
Toll of bond is calculated using the formula given below
Bail Price = ∑(Cnorth/ (1+YTM)due north )+ P / (i+i)n
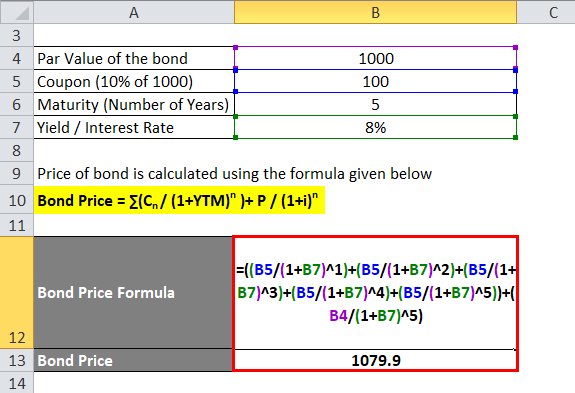
- Bond Price = 100 / (i.08) + 100 / (i.08) ^2 + 100 / (1.08) ^3 + 100 / (1.08) ^4 + 100 / (1.08) ^5 + 1000 / (1.08) ^ 5
- Bond Toll = 92.6 + 85.seven + 79.4 + 73.five + 68.02 + 680.58
- Bond Price = Rs 1079.9
Bond Pricing Formula – Example #2
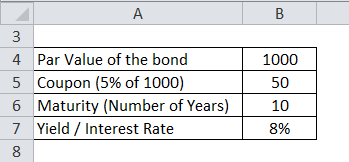
Permit's calculate the price of a Reliance corporate bail which has a par value of Rs 1000 and coupon payment is 5% and yield is 8%. The maturity of the bond is x years
Toll of bond is calculated using the formula given below
Bond Price = ∑(Cn/ (ane+YTM)due north )+ P / (1+i)n
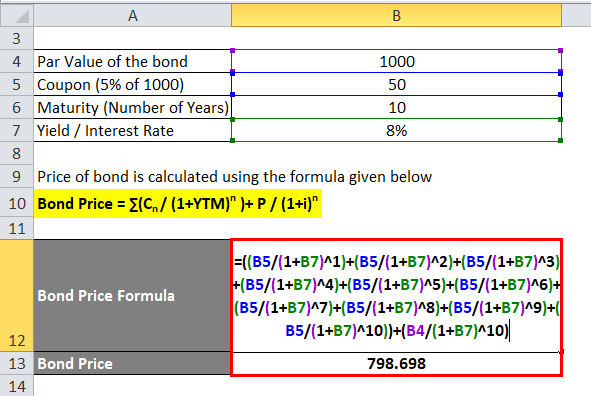
- Bond Toll = 50 / (1.08) + 50 / (1.08) ^2 + 50 / (i.08) ^three + l / (1.08) ^iv + l / (1.08) ^5 + 50 / (i.08) ^6 + l / (1.08) ^7 + fifty / (1.08) ^8 + 50 / (1.08) ^9 + 50 / (1.08) ^x + 1000 / (1.08) ^ 10
- Bond Price = 46.3 + 42.87 + 39.69 + 36.75 + 34.03 + 31.51 + 29.17 + 27.01 + 25.01 + 23.16 + 463.19
- Bail Price = Rs 798.698
Bond Pricing Formula – Example #3
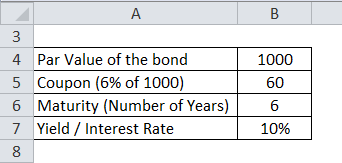
Let'southward calculate the price of a Tata Corp. corporate bond which has a par value of Rs chiliad and coupon payment is half-dozen% and yield is 10%. The maturity of the bond is six years
Price of bond is calculated using the formula given beneath
Bond Price = ∑(Cnorthward/ (1+YTM)n )+ P / (1+i)n
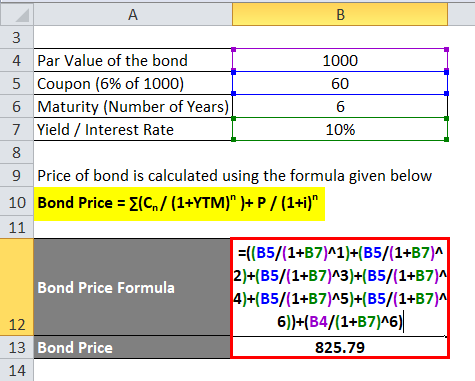
- Bond Cost = 60 / (1.1) + 60 / (1.1) ^two + sixty / (1.ane) ^3 + sixty / (one.1) ^iv + 60 / (i.i) ^5 + 60 / (i.1) ^6 + one thousand / (1.ane) ^ 6
- Bond Toll = 54.55 + 49.59 + 45.08 + 40.98 + 37.26 + 33.87 + 564.47
- Bond Toll = Rs 825.79
Explanation of Bond Pricing Formula
As tin can be seen from the Bond Pricing formula, in that location are 4 factors that tin can affect the bond prices. The factors are illustrated below: –
- Par Value or Confront Value (P) – This is the actual money that is being borrowed by the lender or purchaser of bonds. Generally, information technology is 100 or m per nay bail. The chief corporeality borrowed by the lender is the number of bonds purchased multiplied by the par value.
- Tenor or Years of Maturity (n) – This describes the number of years that it takes for whatsoever bond to mature or when the issuer of bonds volition render the par value to the purchaser of bonds.
- Yield to Maturity (YTM) – This can be described as the rate of return that the purchaser of a bail will become if the investor holds the bond till its maturity. As well, this could be the prevailing interest rate to calculate the current market price of the bond.
- Coupon Rate (C) – This is the periodic payment, ordinarily one-half-yearly or yearly, given to the purchaser of the bonds as interest payments for purchasing the bonds from the issuer.
The bond prices are so calculated using the concept of Time Value of Money wherein each coupon payment and after, the primary payment is discounted to their present value based on the prevailing interest rates.
Relevance and Uses of Bail Pricing Formula
The bond prices are afflicted past the above mentioned factors and some of the points to recall are: –
- Whatsoever bail which has a higher coupon payment volition have a higher price
- Any bond which has a college par value will have a higher cost
- Whatever bail which has a higher years to maturity will have a higher price
- Any bond which has a higher yield to maturity will accept a lower price
These mentioned factors affect the bonds in the primary marketplace. There are other factors which affect the bond prices in the secondary market. They are: –
- Credit rating or creditworthiness of the issuer of bonds
- Liquidity of the secondary market place for bonds
- Time for the next payment of bonds
Bonds issued by regime or corporates are rated by rating agencies like S&P, Moody's, etc. based on the creditworthiness of issuing firm. The ratings vary from AAA (highest credit rating) to D (junk bonds) and based on the rating the yield to maturity varies. The higher rated bonds volition offer a lower yield to maturity. Bonds which are traded a lot and volition accept a college price than bonds that are rarely traded. Fourth dimension for side by side payment is used for coupon payments which apply the muddy pricing theory for bonds. The muddy price of a bond is coupon payment plus accrued interest over the catamenia. Every bit the coupon disbursal date gets closer, bondholder has to await lesser fourth dimension to receive his payment hence one needs to provide added incentive to brand that bondholder sell his bond which drives up need and hence increases the prices of bonds.
Conclusion
Bail pricing formula depends on factors such as a coupon, yield to maturity, par value and tenor. These factors are used to calculate the price of the bail in the main market. In the secondary market, other factors come into play such as creditworthiness of issuing firm, liquidity and time for next coupon payments.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Bond Pricing formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate Bail Pricing forth with applied examples. Nosotros also provide downloadable excel template. You may too wait at the following articles to learn more –
- What is Working Capital Turnover Ratio Formula?
- Coupon Rate Formula
- Bacon Formula
- Daily Compound Interest Formula
- Turnover Ratio Formula | Examples | Excel Template
edwardsanardeakin.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.educba.com/bond-pricing-formula/
0 Response to "how to know what table value to use bond price issue"
Postar um comentário